鉄合金精製炉と小樽精製炉の違い
鉄金加工過程において,鉄合金精製炉とラッドル精製炉 (LRF) は,精製のための重要な設備として機能します.しかし,技術的な目的では大きく異なります.運用原理や応用分野について

1技術の目的と最終製品
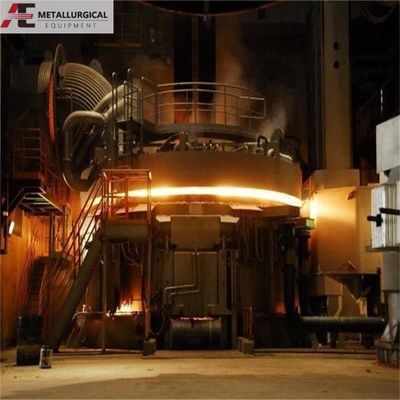
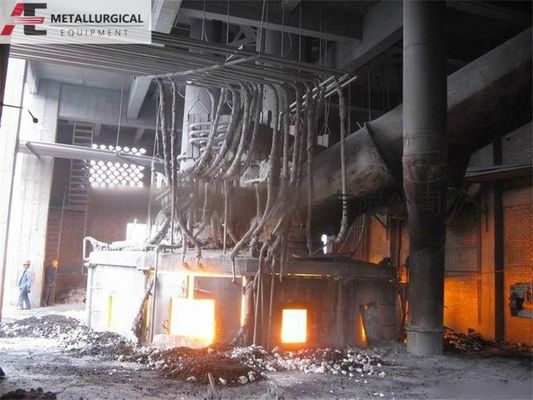
鉄合金精製炉(電弧炉型)
主な目的は鉱石,高シリコン低炭素フェロ合金再融製品,および流体精製である.コアプロセスは,中炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低炭素,低微型炭酸鉄合金本質的に特定の鉄合金製品のための生産ユニットです.生産は,原料の周期的な充電と最終合金へのタッピングを含む,バッチ (間歇的) プロセスで特徴づけられています..
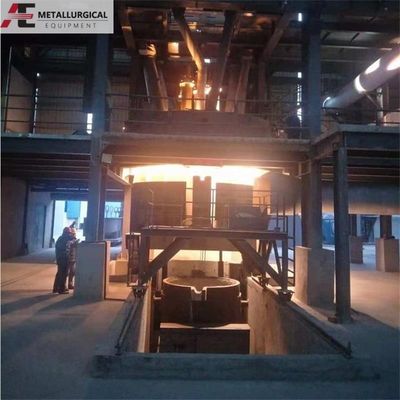
ラッドル精製炉(LRF)
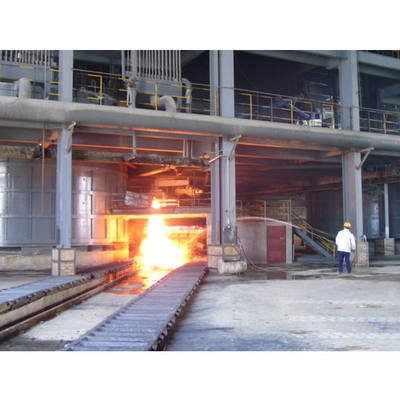
これは,原炉 (電気弧炉,基本酸素炉,またはオープンホートなど) から溶融した鋼を精製するように設計されています.その主な機能は,二次精製,温度制御,鉄鋼製造と連続鋳造/ローリングの間の調整のためのプロセスバッファとして機能LRFは溶融装置ではなく,重要な二次または外部精製装置です. 精密な組成,温度,清潔性を達成するために,溶融した鋼を処理します.
2プロセスと運用特性
鉄合金精製炉:
プロセス: 酸化除去 (主にシリコン) のためのスラグ金属反応に焦点を当てています. 異なるバッチで動作します.
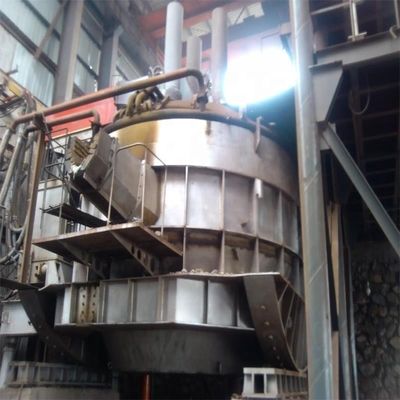
オーブンの種類:通常は,低煙蓋付きのオープントップ,カバー,半封閉型を含む.オーブンのボディは固定,傾斜,または回転することができます.
主要システム: 炉殻,屋根/フット,電極システム,充電システム,水力システム,水冷却システムからなる.
洗浄炉:
プロセス: 複数の高度な精製機能を1つのステーションに統合する:
1弧熱と温度管理: 溶融鋼の再熱と温度均一化を可能にし,合金添加,組成トリミング,スラグ状態調整を可能にします.深層脱硫脱酸化する
2惰性ガス混ぜ: 通常は,温度と組成を均一化し,スラグ金属反応を促進し,挿入物を除去するために,小鉢底の多孔プラグを通して注入されたアルゴンを使用します.
3真空脱ガス: LF-VDまたは類似の組み合わせで用いられる. プースは真空蓋の下に置かれ,水素と窒素のようなガスは真空ポンプ (例えば蒸気噴射機) によって除去される.通常はアルゴンを混ぜてさらに脱酸素化や脱硫化のために強化される..
主要システム: 鍋 (炉体として作用する),電極付きの移動式屋根 (加熱用),アルゴンの乱すシステム,真空システム (装備されている場合),合金/添加物供給システム,複雑なプロセス制御システム.
3生産流における応用と役割
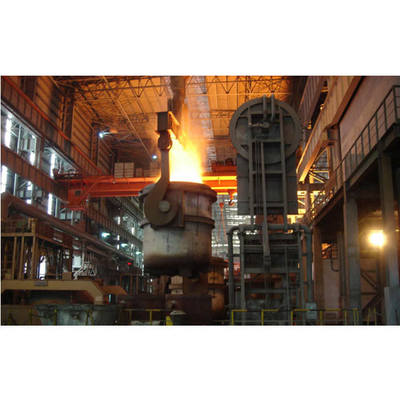
鉄合金精製炉: 鉄合金工場における主要な生産コアとして機能する.その製品が完成した鉄合金で,その後鋼鉄製造に添加物として使用されます.
ラッドル精製炉: 鉄鋼工場内の重要なバッファと精製ステーションとして,原鋼製造と連続鋳造の間に位置する.統合工場への主な利点には,:
精製/鋳造の必要性から原発溶融を切り離すことで,全体的な生産リズムを加速する.
金属効率と製品の質 (清潔性,均質性,正確な組成) の向上
絶え間ない鋳造のための最適で安定した温度を保証し,板質を向上させる.
4. 運用安全に焦点を当て
LRFの標準運転手順は,次のような,プライマリフェロ合金炉とは異なる重要な安全性側面を強調する.
操作前の厳格な検査は,車輪の鍵,移動スイッチ,およびすべての機械/補助システム (真空,ガス,暖房,給水) にあります.
高電圧の電気安全プロトコルの厳格な 電気電極の操作と電源伝送
真空操作,酸素吹き込み (油のない手袋が必要) およびアルゴン混ぜのための特殊手順.
暖房ゲンターなどの高層構造物での保守中に必須の隔離 (キーロックアウト) とクリアメント手順
比較表の要約

結論として,両者は"精製"を伴うが,鉄合金精製炉は,合金生産のための主要な溶融/精製ユニットである.ラドル精製炉は,質の向上のために設計された洗練された後処理装置です.鋼鉄生産の精度と効率を
我々は,専門的な電気オーブンの製造者です.さらなる問い合わせのために,またはあなたが浸水弧炉,電気弧炉,小鉢精製炉,または他の溶融設備を必要とします.連絡してください.スーザン@aeaxa.com

 メッセージは20〜3,000文字にする必要があります。
メッセージは20〜3,000文字にする必要があります。 メールを確認してください!
メールを確認してください!  メッセージは20〜3,000文字にする必要があります。
メッセージは20〜3,000文字にする必要があります。 メールを確認してください!
メールを確認してください! 








